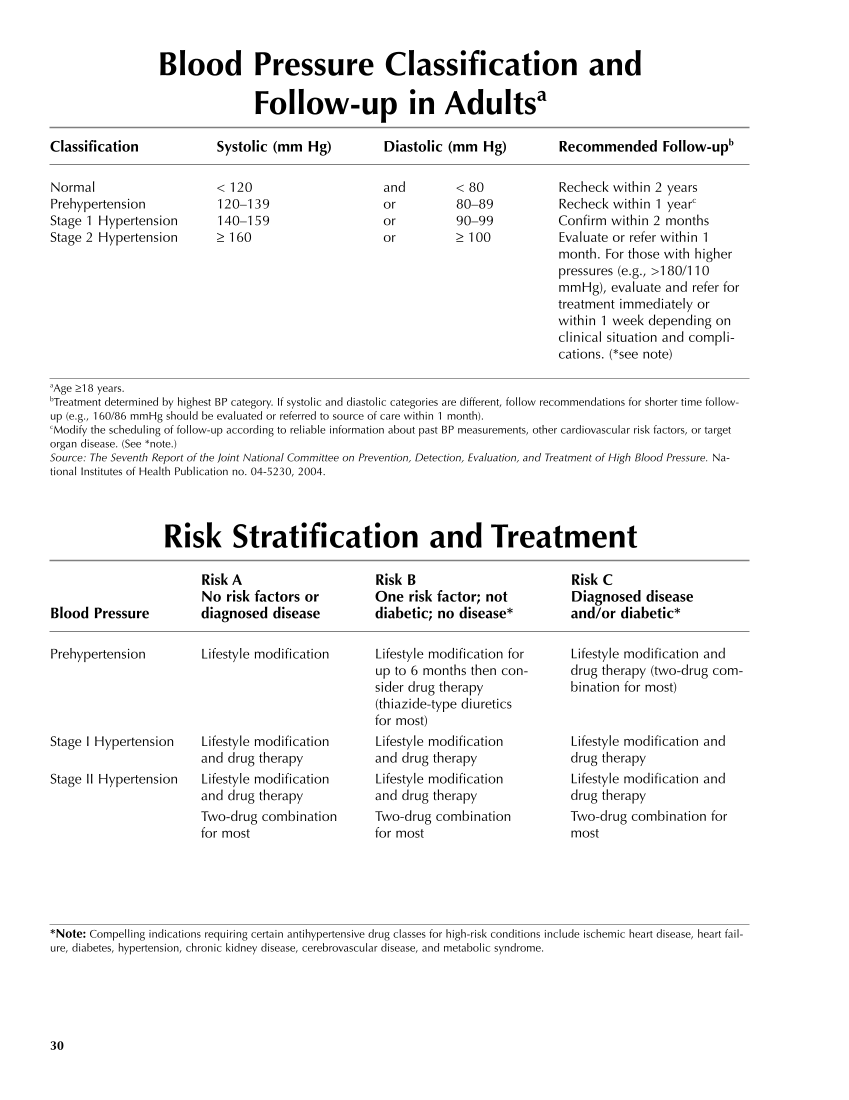
30 Blood Pressure Classification and Follow-up in Adultsa Classification Systolic (mm Hg) Diastolic (mm Hg) Recommended Follow-upb Normal 120 and 80 Recheck within 2 years Prehypertension 120–139 or 80–89 Recheck within 1 yearc Stage 1 Hypertension 140–159 or 90–99 Confirm within 2 months Stage 2 Hypertension ≥ 160 or ≥ 100 Evaluate or refer within 1 month. For those with higher pressures (e.g., 180/110 mmHg), evaluate and refer for treatment immediately or within 1 week depending on clinical situation and compli- cations. (*see note) a Age ≥18 years. b Treatment determined by highest BP category. If systolic and diastolic categories are different, follow recommendations for shorter time follow- up (e.g., 160/86 mmHg should be evaluated or referred to source of care within 1 month). c Modify the scheduling of follow-up according to reliable information about past BP measurements, other cardiovascular risk factors, or target organ disease. (See *note.) Source: The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Na- tional Institutes of Health Publication no. 04-5230, 2004. Risk Stratification and Treatment Risk A Risk B Risk C No risk factors or One risk factor not Diagnosed disease Blood Pressure diagnosed disease diabetic no disease* and/or diabetic* Prehypertension Lifestyle modification Stage I Hypertension Lifestyle modification and drug therapy Stage II Hypertension Lifestyle modification and drug therapy Two-drug combination for most *Note: Compelling indications requiring certain antihypertensive drug classes for high-risk conditions include ischemic heart disease, heart fail- ure, diabetes, hypertension, chronic kidney disease, cerebrovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome. Lifestyle modification for up to 6 months then con- sider drug therapy (thiazide-type diuretics for most) Lifestyle modification and drug therapy Lifestyle modification and drug therapy Two-drug combination for most Lifestyle modification and drug therapy (two-drug com- bination for most) Lifestyle modification and drug therapy Lifestyle modification and drug therapy Two-drug combination for most
Purchased from OEM Press by (ge corporate access). (C) 2013 OEM Health Information, Inc. All rights reserved.