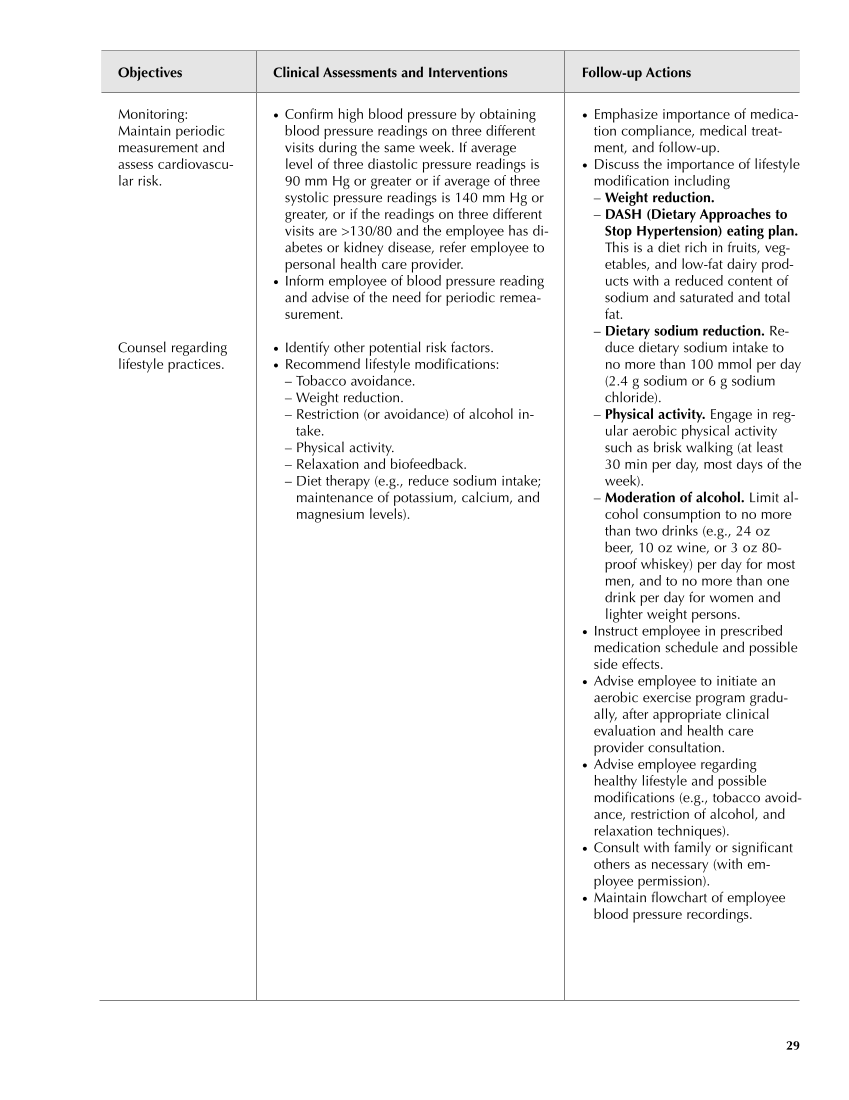
● Emphasize importance of medica- tion compliance, medical treat- ment, and follow-up. ● Discuss the importance of lifestyle modification including – Weight reduction. – DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) eating plan. This is a diet rich in fruits, veg- etables, and low-fat dairy prod- ucts with a reduced content of sodium and saturated and total fat. – Dietary sodium reduction. Re- duce dietary sodium intake to no more than 100 mmol per day (2.4 g sodium or 6 g sodium chloride). – Physical activity. Engage in reg- ular aerobic physical activity such as brisk walking (at least 30 min per day, most days of the week). – Moderation of alcohol. Limit al- cohol consumption to no more than two drinks (e.g., 24 oz beer, 10 oz wine, or 3 oz 80- proof whiskey) per day for most men, and to no more than one drink per day for women and lighter weight persons. ● Instruct employee in prescribed medication schedule and possible side effects. ● Advise employee to initiate an aerobic exercise program gradu- ally, after appropriate clinical evaluation and health care provider consultation. ● Advise employee regarding healthy lifestyle and possible modifications (e.g., tobacco avoid- ance, restriction of alcohol, and relaxation techniques). ● Consult with family or significant others as necessary (with em- ployee permission). ● Maintain flowchart of employee blood pressure recordings. Objectives Clinical Assessments and Interventions Follow-up Actions 29 Monitoring: Maintain periodic measurement and assess cardiovascu- lar risk. Counsel regarding lifestyle practices. ● Confirm high blood pressure by obtaining blood pressure readings on three different visits during the same week. If average level of three diastolic pressure readings is 90 mm Hg or greater or if average of three systolic pressure readings is 140 mm Hg or greater, or if the readings on three different visits are 130/80 and the employee has di- abetes or kidney disease, refer employee to personal health care provider. ● Inform employee of blood pressure reading and advise of the need for periodic remea- surement. ● Identify other potential risk factors. ● Recommend lifestyle modifications: – Tobacco avoidance. – Weight reduction. – Restriction (or avoidance) of alcohol in- take. – Physical activity. – Relaxation and biofeedback. – Diet therapy (e.g., reduce sodium intake maintenance of potassium, calcium, and magnesium levels). Guideline continues on next page
Purchased from OEM Press by (ge corporate access). (C) 2013 OEM Health Information, Inc. All rights reserved.