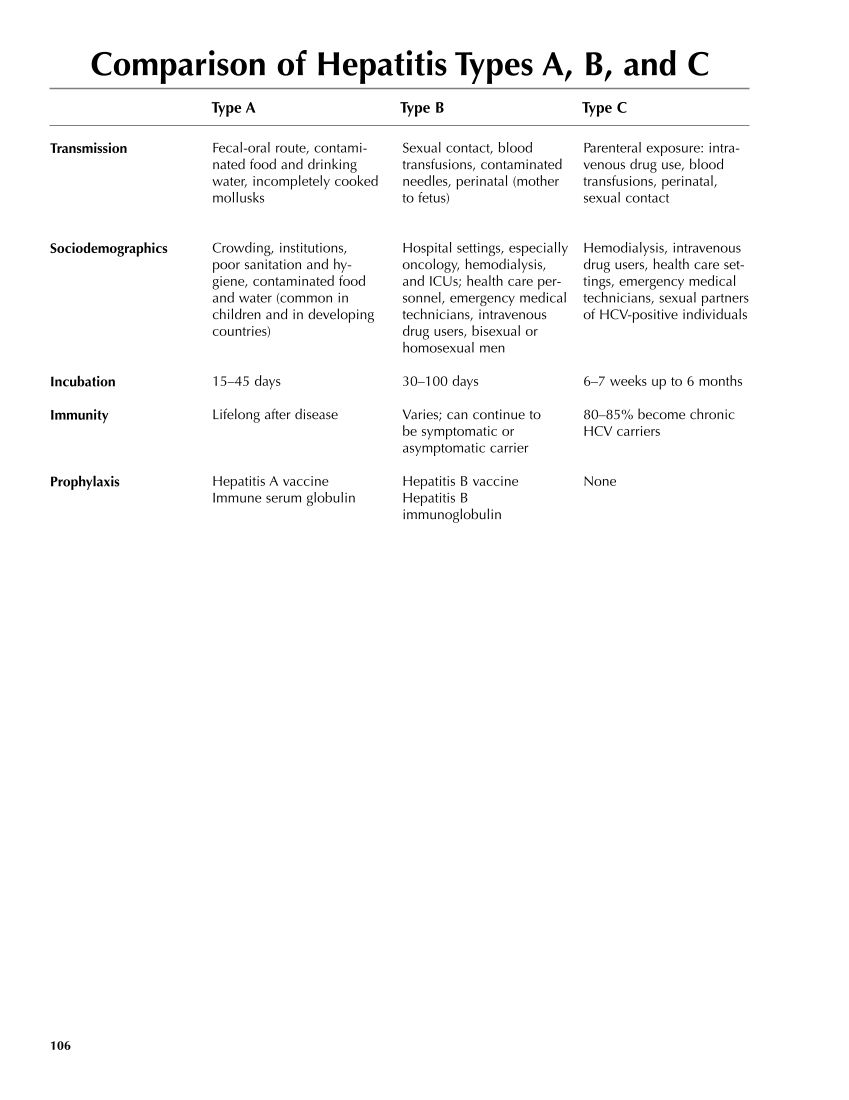
106 Comparison of Hepatitis Types A, B, and C Type A Type B Type C Transmission Sociodemographics Incubation Immunity Prophylaxis Parenteral exposure: intra- venous drug use, blood transfusions, perinatal, sexual contact Hemodialysis, intravenous drug users, health care set- tings, emergency medical technicians, sexual partners of HCV-positive individuals 6–7 weeks up to 6 months 80–85% become chronic HCV carriers None Sexual contact, blood transfusions, contaminated needles, perinatal (mother to fetus) Hospital settings, especially oncology, hemodialysis, and ICUs health care per- sonnel, emergency medical technicians, intravenous drug users, bisexual or homosexual men 30–100 days Varies can continue to be symptomatic or asymptomatic carrier Hepatitis B vaccine Hepatitis B immunoglobulin Fecal-oral route, contami- nated food and drinking water, incompletely cooked mollusks Crowding, institutions, poor sanitation and hy- giene, contaminated food and water (common in children and in developing countries) 15–45 days Lifelong after disease Hepatitis A vaccine Immune serum globulin
Purchased from OEM Press by (ge corporate access). (C) 2013 OEM Health Information, Inc. All rights reserved.