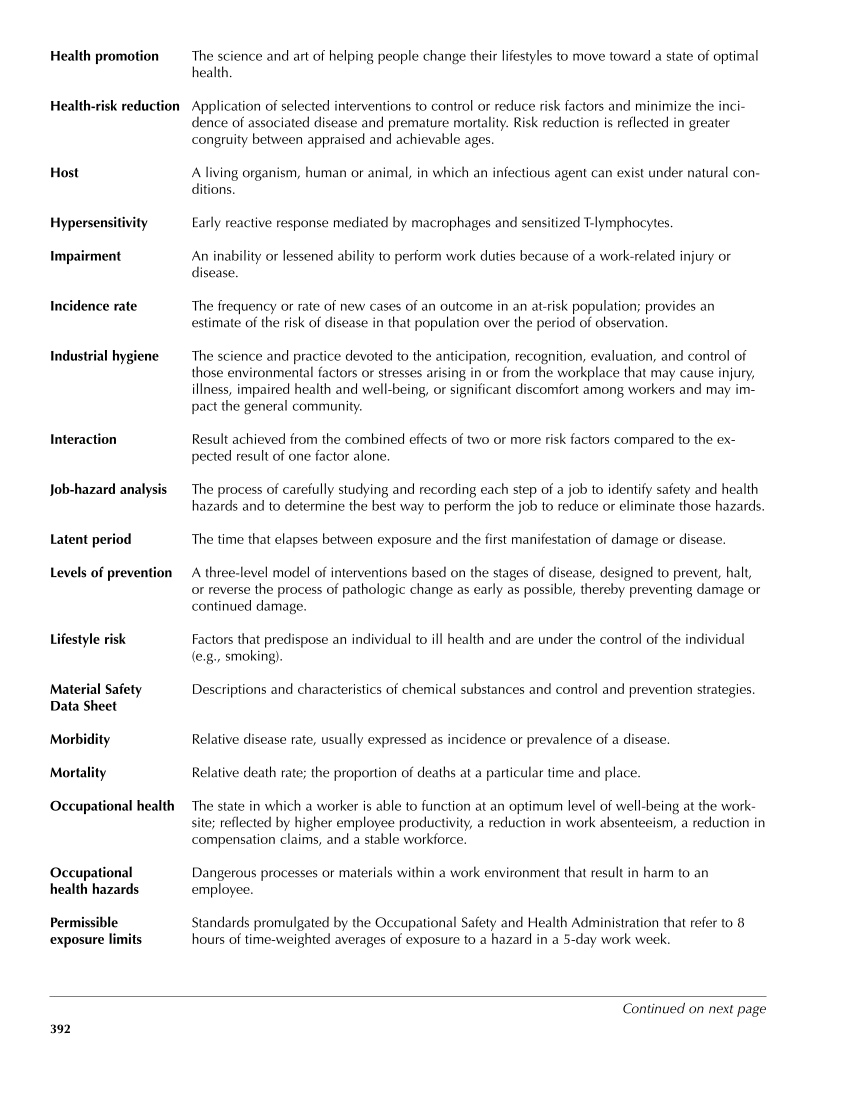
Health promotion The science and art of helping people change their lifestyles to move toward a state of optimal health. Health-risk reduction Application of selected interventions to control or reduce risk factors and minimize the inci- dence of associated disease and premature mortality. Risk reduction is reflected in greater congruity between appraised and achievable ages. Host A living organism, human or animal, in which an infectious agent can exist under natural con- ditions. Hypersensitivity Early reactive response mediated by macrophages and sensitized T-lymphocytes. Impairment An inability or lessened ability to perform work duties because of a work-related injury or disease. Incidence rate The frequency or rate of new cases of an outcome in an at-risk population provides an estimate of the risk of disease in that population over the period of observation. Industrial hygiene The science and practice devoted to the anticipation, recognition, evaluation, and control of those environmental factors or stresses arising in or from the workplace that may cause injury, illness, impaired health and well-being, or significant discomfort among workers and may im- pact the general community. Interaction Result achieved from the combined effects of two or more risk factors compared to the ex- pected result of one factor alone. Job-hazard analysis The process of carefully studying and recording each step of a job to identify safety and health hazards and to determine the best way to perform the job to reduce or eliminate those hazards. Latent period The time that elapses between exposure and the first manifestation of damage or disease. Levels of prevention A three-level model of interventions based on the stages of disease, designed to prevent, halt, or reverse the process of pathologic change as early as possible, thereby preventing damage or continued damage. Lifestyle risk Factors that predispose an individual to ill health and are under the control of the individual (e.g., smoking). Material Safety Descriptions and characteristics of chemical substances and control and prevention strategies. Data Sheet Morbidity Relative disease rate, usually expressed as incidence or prevalence of a disease. Mortality Relative death rate the proportion of deaths at a particular time and place. Occupational health The state in which a worker is able to function at an optimum level of well-being at the work- site reflected by higher employee productivity, a reduction in work absenteeism, a reduction in compensation claims, and a stable workforce. Occupational Dangerous processes or materials within a work environment that result in harm to an health hazards employee. Permissible Standards promulgated by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration that refer to 8 exposure limits hours of time-weighted averages of exposure to a hazard in a 5-day work week. 392 Continued on next page
Purchased from OEM Press by (ge corporate access). (C) 2013 OEM Health Information, Inc. All rights reserved.