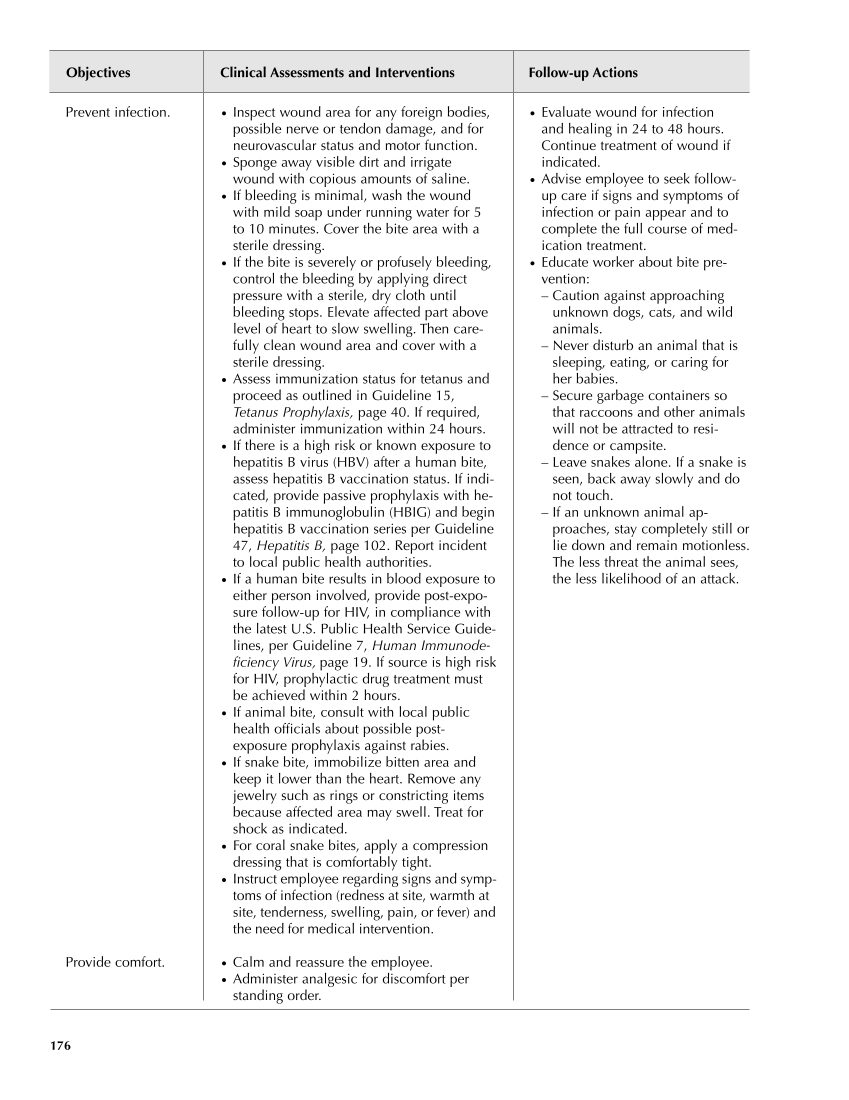
Objectives Clinical Assessments and Interventions Follow-up Actions 176 ● Evaluate wound for infection and healing in 24 to 48 hours. Continue treatment of wound if indicated. ● Advise employee to seek follow- up care if signs and symptoms of infection or pain appear and to complete the full course of med- ication treatment. ● Educate worker about bite pre- vention: – Caution against approaching unknown dogs, cats, and wild animals. – Never disturb an animal that is sleeping, eating, or caring for her babies. – Secure garbage containers so that raccoons and other animals will not be attracted to resi- dence or campsite. – Leave snakes alone. If a snake is seen, back away slowly and do not touch. – If an unknown animal ap- proaches, stay completely still or lie down and remain motionless. The less threat the animal sees, the less likelihood of an attack. Prevent infection. Provide comfort. ● Inspect wound area for any foreign bodies, possible nerve or tendon damage, and for neurovascular status and motor function. ● Sponge away visible dirt and irrigate wound with copious amounts of saline. ● If bleeding is minimal, wash the wound with mild soap under running water for 5 to 10 minutes. Cover the bite area with a sterile dressing. ● If the bite is severely or profusely bleeding, control the bleeding by applying direct pressure with a sterile, dry cloth until bleeding stops. Elevate affected part above level of heart to slow swelling. Then care- fully clean wound area and cover with a sterile dressing. ● Assess immunization status for tetanus and proceed as outlined in Guideline 15, Tetanus Prophylaxis, page 40. If required, administer immunization within 24 hours. ● If there is a high risk or known exposure to hepatitis B virus (HBV) after a human bite, assess hepatitis B vaccination status. If indi- cated, provide passive prophylaxis with he- patitis B immunoglobulin (HBIG) and begin hepatitis B vaccination series per Guideline 47, Hepatitis B, page 102. Report incident to local public health authorities. ● If a human bite results in blood exposure to either person involved, provide post-expo- sure follow-up for HIV, in compliance with the latest U.S. Public Health Service Guide- lines, per Guideline 7, Human Immunode- ficiency Virus, page 19. If source is high risk for HIV, prophylactic drug treatment must be achieved within 2 hours. ● If animal bite, consult with local public health officials about possible post- exposure prophylaxis against rabies. ● If snake bite, immobilize bitten area and keep it lower than the heart. Remove any jewelry such as rings or constricting items because affected area may swell. Treat for shock as indicated. ● For coral snake bites, apply a compression dressing that is comfortably tight. ● Instruct employee regarding signs and symp- toms of infection (redness at site, warmth at site, tenderness, swelling, pain, or fever) and the need for medical intervention. ● Calm and reassure the employee. ● Administer analgesic for discomfort per standing order. Guideline continues on next page
Purchased from OEM Press by (ge corporate access). (C) 2013 OEM Health Information, Inc. All rights reserved.